1. Reasons of Conflicts
- Israel – Iran conflicts over the years over religious and ideological differences fueled mutual distrust and animosity to proxy conflicts to Nuclear threats.
- Iran’s Support for Anti-Israel Groups such as Hamas, Hezbollah, Houthi who are labeled as terrorist organizations by Israel.
- Israel viewing Iran’s nuclear programme as a serious threat, fearing the development of nuclear weapons that could endanger its existence.
2. Iran’s Nuclear Aspirations
Iran insists its nuclear program is for peaceful purposes—mainly energy production and medical research. It is a signatory to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), which allows for civilian nuclear development under international oversight; but
- rejecting IAEA conclusions of enriched uranium to levels,
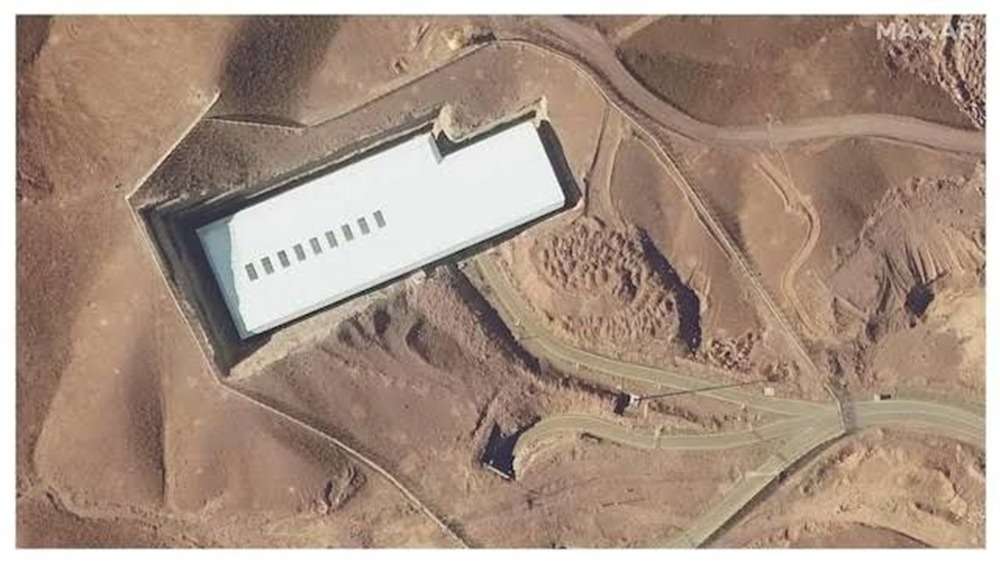
- underground facilities like Fordow,
- covert weapons programs,
3. US – Israel Coalition
- Failed talks on Nuclear issues between US- Iran from 2015 and growing Iran Nuclear ambitions led to reinforcing its stance that Iran’s nuclear program poses an existential threat.
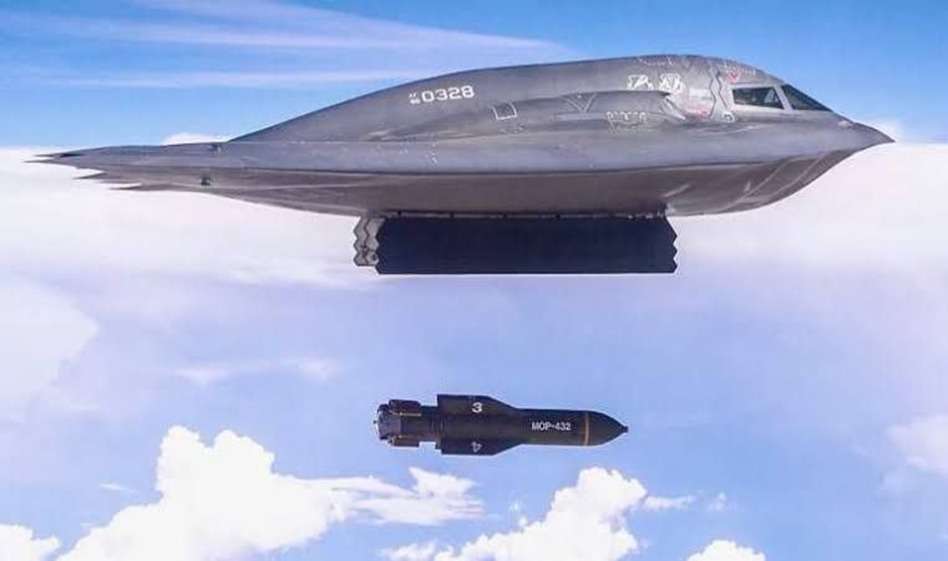
- The S. successfully targeted deeply buried nuclear infrastructure targeting three of Iran’s key nuclear sites—Fordow, Natanz, and Isfahan. Conducted using B-2 stealth bombers equipped with GBU-57 bunker-busting bombs.

GBU-57 or Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP)
The most powerful non-nuclear bomb in the U.S. arsenal—designed specifically to destroy deeply buried and fortified targets like underground nuclear facilities.
Weight: 30,000 pounds (13,600 kg)
Length: Over 20 feet (6.2 meters)
Guidance System: GPS and inertial navigation for precision targeting.

4.Israel – Iran Conflict pose a Major Threat.
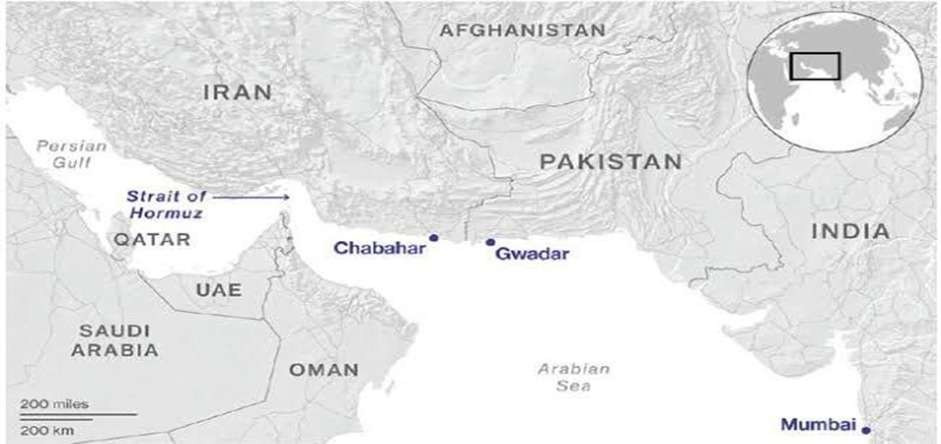
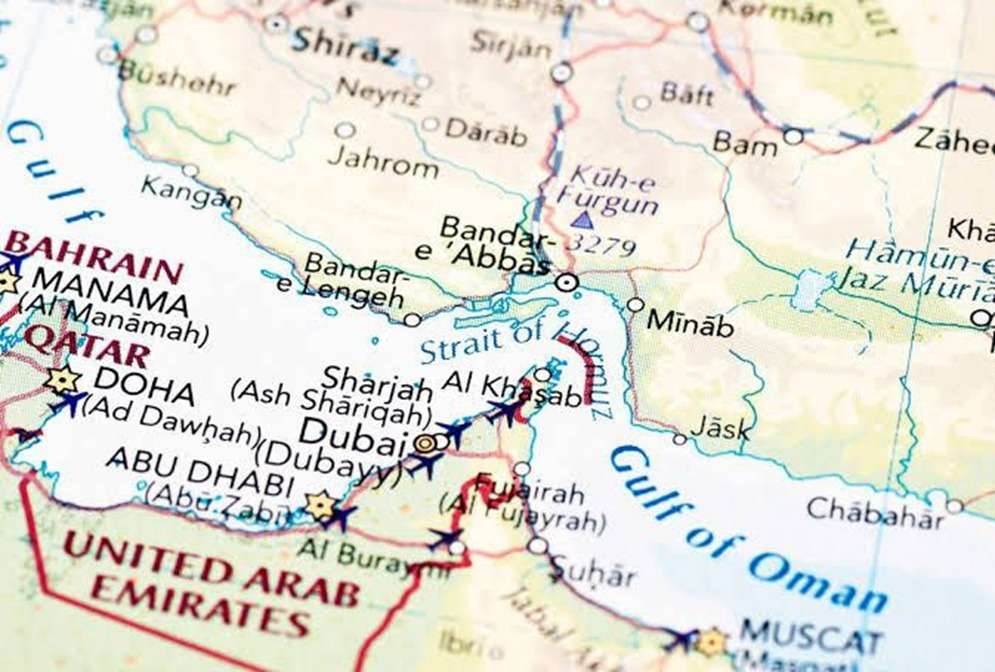
- The Strait of Hormuz is one of the world’s most important shipping routes, and its most vital oil transit choke point bordering Iran to its north who have always threatened to block it at its narrowest point, the Strait of Hormuz and its shipping lanes lie entirely within Iran.
- The strait is deep enough for the world’s biggest crude oil tankers, and is used by the major oil and gas producers in the Middle East – and their customers including India.
- It would have direct consequences on world markets as it will soar up the oil prices and also to Gulf countries whose economies rely heavily on energy exports.
- Inflated oil prices will give effect to rising manufacturing costs could eventually be passed on to consumers, fuelling inflation around the world.
5.India’s Stance on the Conflict
- India has always reiterated a Non- Aligned stance which is the result of a delicate balancing act stretching back many years.
- India maintains a healthy relation with both Israel Iran as they both provide India strategical, technological and economical parameters crucial for fostering Indian Development.
Israel’s importance for India
- Israel is one of India’s top defense suppliers, providing cutting-edge technologies like drones, missile systems and surveillance equipment. The two countries also collaborate on joint military training and counter-terrorism intelligence sharing, especially valuable given India’s security challenges.
2. Through the India-Israel Agricultural Project, Israeli expertise in drip irrigation, water recycling, and desert farming has helped boost India’s agricultural productivity.
3. Both nations share concerns over terrorism and regional instability and technological innovation like cybersecurity, AI, space tech, and biotechnology.
4. Israel is the 3rd largest business partner of India holding key economic importance for India.
Iran’s importance for India
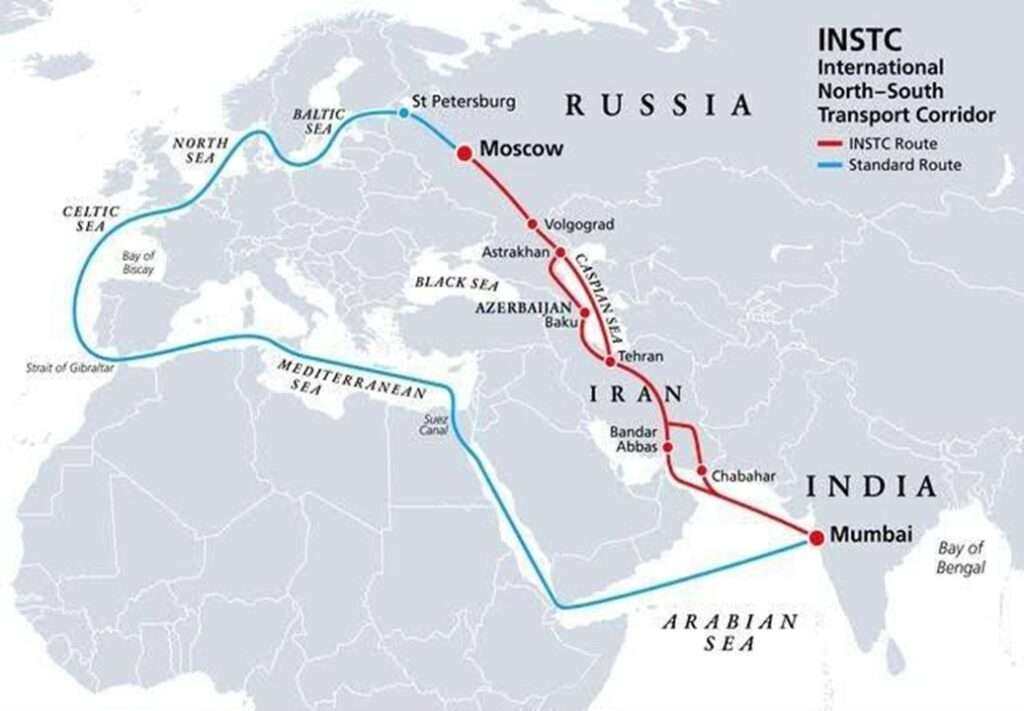
- India has invested heavily in Chabahar Port, a deep-water seaport in southeastern Iran. It gives India direct access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, bypassing Pakistan. This port is also a key node in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), linking India to Russia and Europe via Iran.
2. Iran was India’s third-largest oil supplier, providing nearly 12% of its crude oil needs. With one of the world’s largest reserves of oil and natural gas, Iran remains a potential long-term energy partner if sanctions ease.
3. India exports Basmati rice, tea, and pharmaceuticals to Iran, and imports dry fruits and chemicals & nations also share deep civilizational and cultural ties, including centuries of Persian influence on Indian art, language, and architecture.
6.Nuclear Suppliers Group & International Atomic energy Agency Stance
Nuclear Suppliers Group
The NSG, a 48-nation body that controls the export of nuclear materials and technology, does not issue public statements on geopolitical conflicts. However, its members—especially the U.S., France, and Russia—are deeply involved in shaping nuclear diplomacy. The group’s main concern is preventing nuclear proliferation, and the current conflict has raised alarms about Iran’s potential withdrawal from the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), which would undermine NSG norms.
International Atomic Energy Agency
IAEA has been vocal and deeply concerned that military strikes on nuclear facilities risk radiological disasters. IAEA addressed the UN Security Council, urging all parties to cease hostilities and emphasized that the global non-proliferation regime is at risk.